⚙️ Unified Diffusion-based Planner
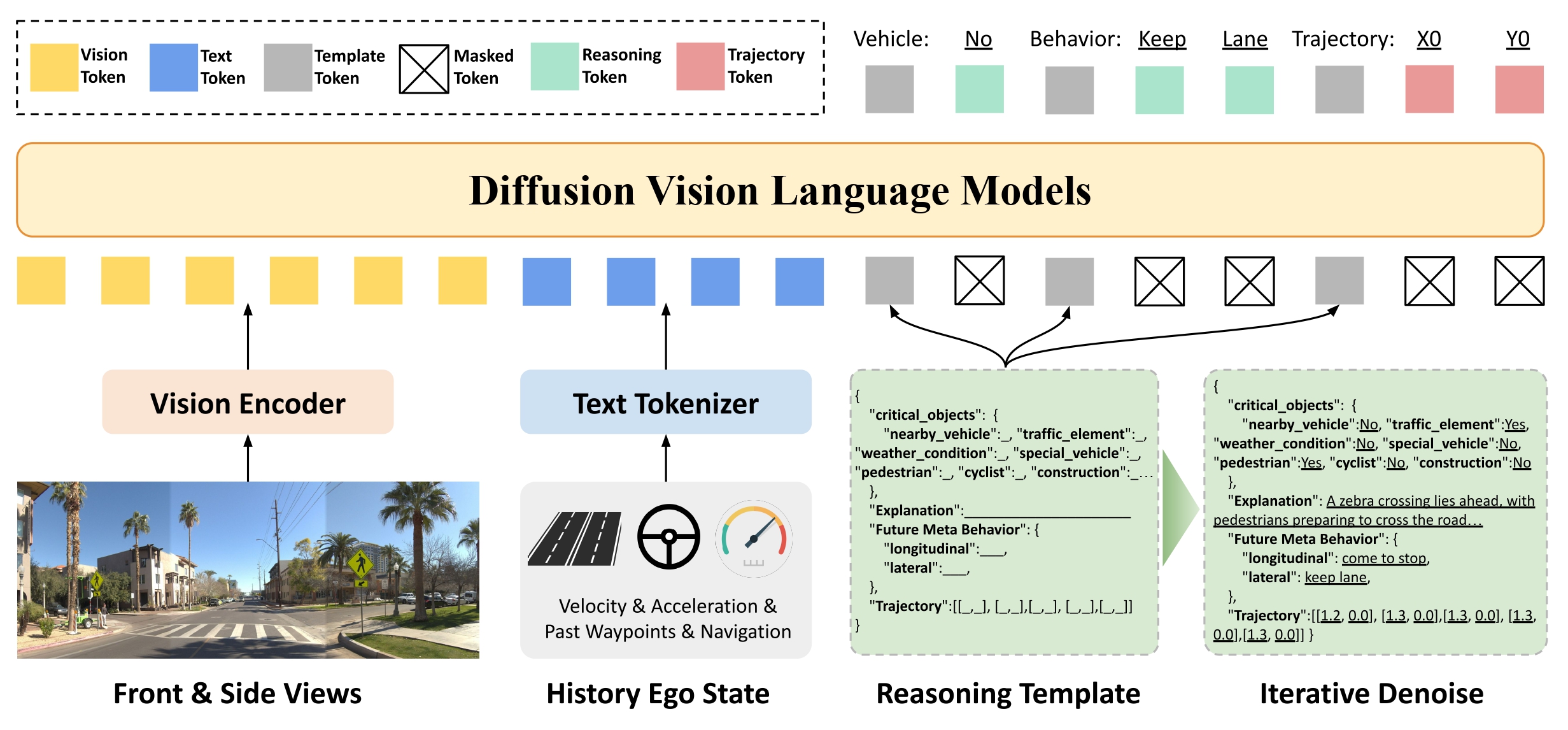
dVLM-AD starts from a structured chain-of-thought template that includes critical objects, causal explanations, future meta behavior, and a sequence of waypoints.
Instead of left-to-right decoding, a diffusion denoiser iteratively refines all reasoning and action tokens jointly, conditioned on multi-camera views, navigation commands, and ego state.
🧩 Controllable Structured Reasoning
During decoding, only editable slots in the template are masked and updated, so the schema itself enforces safety and format constraints.
A dynamic denoise strategy with a special reduce token allows variable-length phrases inside fixed windows, avoiding length-matching bias and preserving semantic consistency between behavior and trajectory.
🪜 Two Training Stages
Stage I aligns the diffusion backbone to the driving domain using about 145k driving-related QA pairs from existing datasets, grounding perception and prediction in realistic scenes.
Stage II supervises structured reasoning–action pairs on nuScenes and WOD-E2E (23k + 30k samples), so that object detection, explanations, meta behaviors, and trajectories are learned to stay consistent.